Ada berapa jumlah bintang di galaksi
Bimasakti? Baru-baru ini, para ilmuwan telah mengeluarkan katalog baru
bagian utara Galaksi Bimasakti, termasuk didalamnya prediksi benda
langit bersinar yang tak kurang dari 219 juta bintang.
Kita tak akan mampu menafsirkan jumlah
bintang di Galaksi Bimasakti, tapi dengan menggunakan cermin 2,5 M yang
dimiliki INT atau Newton Telescope Ishak, para ilmuwan berhasil memetakan 219 juta bintang Bimasakti yang terpisah.
Program INT memetakan semua bintang lebih
terang dari magnitudo ke-20, atau sekitar 1 juta kali lebih redup dari
yang bisa dilihat dengan mata manusia.
Geert Barentsen seorang ilmuwan dari University of Hertfordshire, bersama timnya mengumpulkan katalog dalam program yang dijalani selama sepuluh tahun.
 |
| Tampak taburan bintang yang merupakan bagian dari galaksi tempat Matahari dan Bumi berada, Galaksi Bimasakti. |
Tim gabungan ini menggunakan peralatan khusus yang terpasang pada Newton Telescope Ishak (INT) di La Palma, Kepulauan Canary. Hasil studi pemetaan 219 juta bintang Bimasakti diterbitkan dalam jurnal Royal Astronomical Society edisi September 2014 lalu.
Langit terlihat gelap dari Bumi, galaksi Bimasakti atau bahasa Inggrisnya the Milkyway, terlihat seperti benda besar bersinar yang membentang disepanjang langit.
 |
| Tampak taburan bintang yang memanjang bagai lempeng atau disk kearah bawah dari Galaksi Bimasakti. |
Kalangan astronom menyebutnya sebagai disk
atau ‘lempeng piringan’ dari galaksi kita yang membentang dari ujung
pinggir ke ujung yang lain sepanjang 100,000 tahun cahaya.
Mereka melihat tepi dari sudut pandang orbit Matahari, dimana disk
berisi sebagian besar bintang Bimasakti, termasuk matahari, sebagai
sistim konsentrasi wilayah yang terpadat oleh debu dan gas antariksa.
Dengan menggunakan katalog, para ilmuwan
telah mengumpulkan peta sangat detail dari objek yang berada di galaksi
Bimasakti. Informasi data menunjukkan kepadatan bintang Bimasakti
bervariasi, memberi wawasan baru dan berkembang dalam struktur yang
luas, diantaranya bintang, gas dan debu.
Gambar yang berhasil dihimpun dari peta
kepadatan bintang Bimasakti diperoleh langsung dari katalog teleskop,
data ini menggambarkan pandangan baru yang berhasil diperoleh. Gambaran
ini juga berguna untuk model generasi baru peta Bimasakti.
Katalog galaksi Bimasakti ini diberi nama IPHAS DR2, sebuah data rilis kedua dalam program INT Photometric H-alpha Survey of the Northern Galactic Plane atau IPHAS.
 |
| Black & White – Galaksi Bimasakti bagian utara melalui IPHAS DR2 (klik disini untuk ukuran besar JPG 4500px) (iphas.org) |
 |
| Galaksi Bimasakti bagian utara melalui IPHAS DR2 (klik disini untuk ukuran besar JPG 4500px) (iphas.org) |
Foto Yang Misterius
Dari hasil foto yang diabadikan dan
dirilis ke publik, sepertinya ada keanehan. Beberapa kordinat dan lokasi
atau kawasan banyak yang di ‘blur’ atau dikaburkan gambarnya.
Hal ini menambah kecurigaan banyak
astrologis. Atau memang lokasi-lokasi tersebut masih diteliti oleh
‘pihak-pihak yang berkepentingan’ dalam suatu proyek oleh suatu kelompok
tertentu.
Data ini merupakan contoh dari
eksploitasi astronomi modern dan dianggap sebagai sumber data besar yang
berisi informasi tentang 219 juta bintang Bimasakti yang berhasil
terdeteksi, dimana masing-masing katalog dirangkum dalam 99 atribut.
 |
| Beberapa lokasi dari bagian Bimasakti yang diburamkan atau di ‘blur’ pada foto IPHAS DR2 mengundang misteri. |
Melalui katalog ini, tim ilmuwan juga
menawarkan akses gratis kepada masyarakat dunia untuk pengukuran dalam
studi tertentu. Data ini telah diperoleh melalui dua filter pita lebar
yang berhasil menangkap cahaya merah di ujung galaksi Bimasakti dari
spektrum yang terlihat.
Dan Narrowband teleskop juga menangkap
garis terang tanda-tanda adanya emisi hidrogen, H-alpha. H-alpha
memungkinkan pencitraan terlihat indah pada nebula dan ditemukan dengan
jumlah terbesar dalam disk Bimasakti.
Peta kepadatan bintang Bimasakti
diilustrasikan berdasarkan dari pita gelombang terpanjang yang paling
merah (lihat hasil foto animasi dibawah), di mana efek penggelapan debu
dimoderasi dengan cara meningkatkan gambar struktur lebih detail.
Hal ini jauh lebih berguna dibandingkan
dengan peta yang dihasilkan dari panjang gelombang pendek berwarna biru.
Jadi untuk saat ini dan kedepannya, astronom dan astrofisika bisa
menggunakan peta bintang Bimasakti untuk menemukan berbagai benda langit
yang masih misterius.
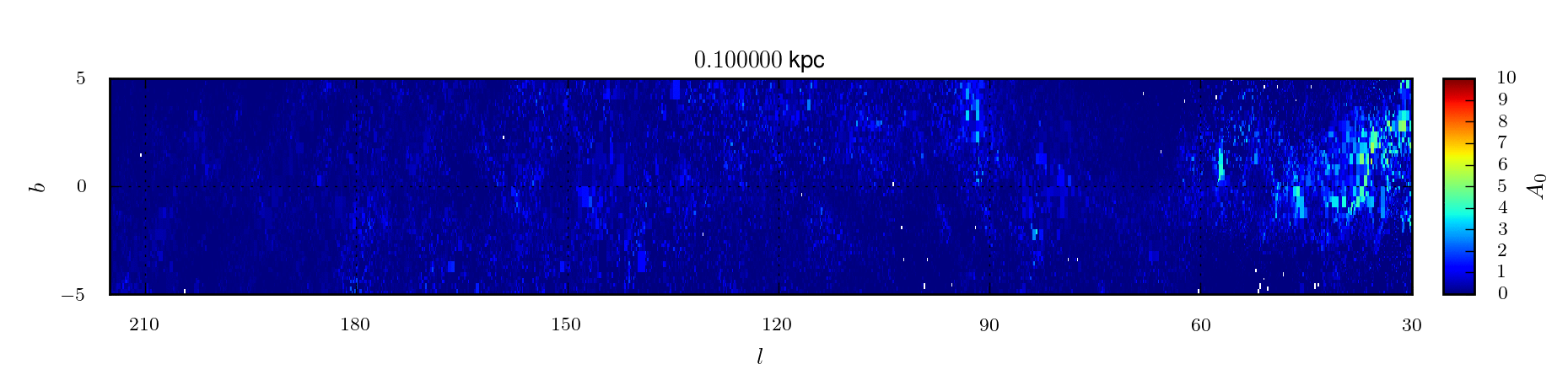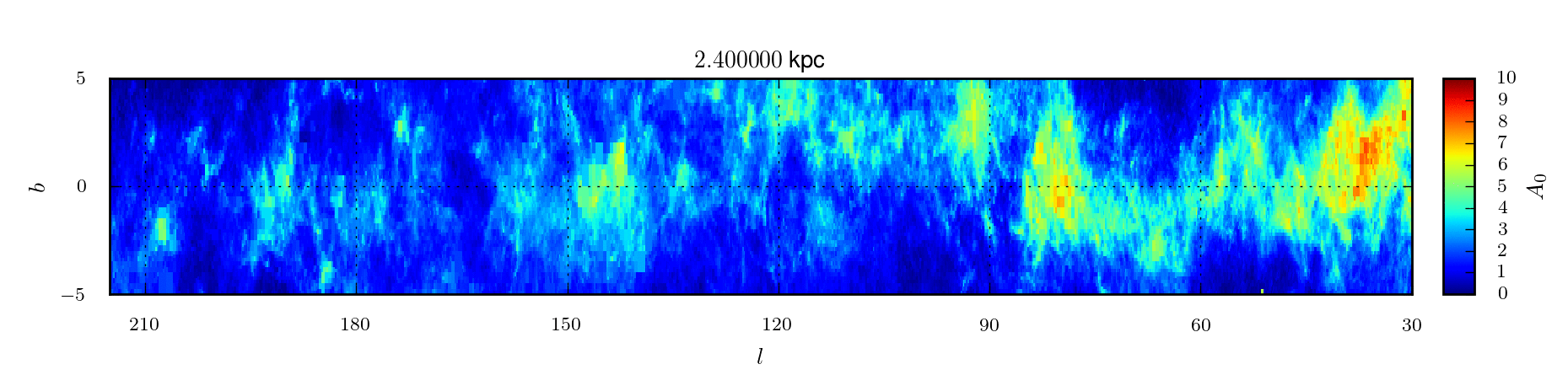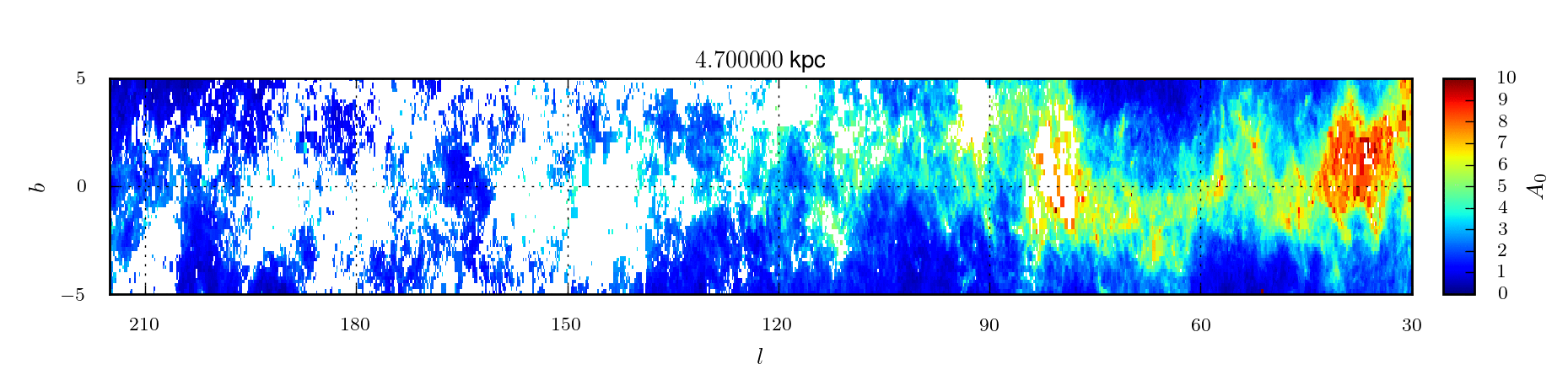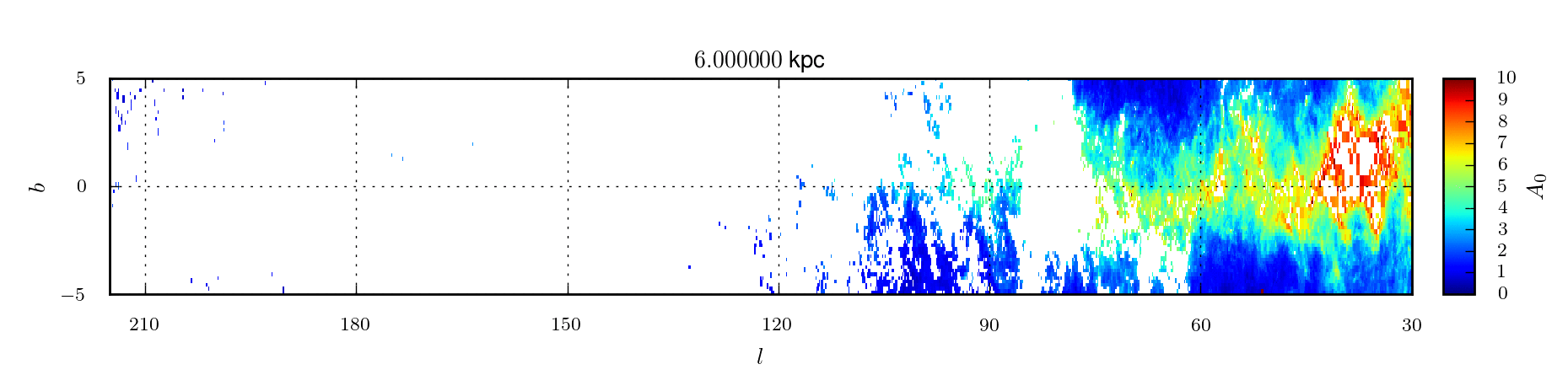
A 3D extinction map of the Northern Galactic Plane based on IPHAS photometry
In Sale et al (2014) we present a 3D extinction map of the entire Northern Galactic Plane (|b| < 5°) based on H-MEAD, an algorithm previously described in Sale (2012), and IPHAS DR2 photometry.
 |
| Animasi Galaksi Bimasakti melalui IPHAS DR2 (klik pada gambar untuk memperbesar) (iphas.org) |
There are two main products available for
download: the 3D extinction map itself and a catalogue of stellar
parameters for the ~38 million stars employed to build the map. They can
be downloaded from this page. In addition, both products will be
available for download from the CDS.
3D map of extinction
The extinction map is presented in two
forms. First, we publish the posterior expectations of mean extinction
and differential extinction for every voxel in the map. These
expectations are accompanied by measurements of the half-widths of 68.3
per cent credible intervals centred on the expectation for both mean
extinction and differential extinction. In addition we also make
available 20 samples from the posterior distribution on the mean
extinction.
Download expectation values
The posterior expectations and uncertainties are available in one large file (107MB)
covering the entire sky, in this form the maximum reliable distance is
indicated in the seventh column. The README accompanying this file
contains column definitions.
Alternatively the same data are available
with one file per sightline. These files detail the Galactic longitude
and latitudes covered in the file header. The individual files are
organised into archives covering 10° wide strips of the Glactic plane.
In this format the final column flags whether a voxel is considered
‘trustworthy’ or not, i.e. if it is within or beyond the maximum
reliable distance for the sightline. The limits of the voxel in Galactic
longitude and latitude are given in the file header. Column definitions
for these files follow after download details.
| Galactic Longitude | Download Catalogue |
|---|---|
| 30° ≤ l < 40° | A_map_030.tar.gz (9 MB) |
| 40° ≤ l < 50° | A_map_040.tar.gz (9 MB) |
| 50° ≤ l < 60° | A_map_050.tar.gz (11 MB) |
| 60° ≤ l < 70° | A_map_060.tar.gz (12MB) |
| 70° ≤ l < 80° | A_map_070.tar.gz (7MB) |
| 80° ≤ l < 90° | A_map_080.tar.gz (6MB) |
| 90° ≤ l < 100° | A_map_090.tar.gz (6MB) |
| 100° ≤ l < 110° | A_map_100.tar.gz (7 MB) |
| 110° ≤ l < 120° | A_map_110.tar.gz (6 MB) |
| 120° ≤ l < 130° | A_map_120.tar.gz (6 MB) |
| 130° ≤ l < 140° | A_map_130.tar.gz (6 MB) |
| 140° ≤ l < 150° | A_map_140.tar.gz (4MB) |
| 150° ≤ l < 160° | A_map_150.tar.gz (5MB) |
| 160° ≤ l < 170° | A_map_160.tar.gz (6MB) |
| 170° ≤ l < 180° | A_map_170.tar.gz (6 MB) |
| 180° ≤ l < 190° | A_map_180.tar.gz (5MB) |
| 190° ≤ l < 200° | A_map_190.tar.gz (5MB) |
| 200° ≤ l < 210° | A_map_200.tar.gz (5 MB) |
| 210° ≤ l < 215° | A_map_210.tar.gz (3 MB) |
Column definitions
| Column | Unit | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| dist | parsec | The distance to the midpoint of the voxel. | |
| mean_A0 | The mean extinction to points within the voxel. Expressed in terms of A0, the monochromatic extinction at 5495 Å. | ||
| sigma_A0 | The differential extinction to the voxel, i.e. the standard deviation of extinction to points within the voxel. Expressed in terms of A0, the monochromatic extinction at 5495 Å. | ||
| d_mean | The halfwidth of a symmetric 68.3% credible interval on mean extinction, centred on the expectation value. This serves as an estimate of the uncertainty on the mean extinction. Expressed in terms of A0, the monochromatic extinction at 5495 Å. | ||
| d_sigma | The halfwidth of a symmetric 68.3% credible interval on differential extinction, centred on the expectation value. This serves as an estimate of the uncertainty on the differential extinction. Expressed in terms of A0, the monochromatic extinction at 5495 Å. | ||
| trustworthy | Indicates whether a voxel is within or beyond the maximum relaible distance. A value of 1 indicates that the voxel is within this distance and can be considered to be trustworthy. A value of 0 indicates that the voxel is beyond this distance and so should not be relied upon. |
Download posterior samples
We also make available 20 samples from
the posterior distribution on mean extinction. For many purposes this
might be a more useful representation of the posterior than that given
by the expectation and halfwidth of the credible interval. We provide
one file for each sightline, where the filename gives the Galactic
longitude and latitude at the centre of the line of sight. The first
column of each file gives the midpoint distance of a voxel, whilst the
subsequent columns each give a value sampled from the posterior on mean
extinction. The samples were all taken from the same set of iterations
in the MCMC chain and so each column is itself a sample from the
posterior on the entire distance extinction relationship.
There is one file for each sightline.
These files detail the Galactic longitude and latitudes covered in the
file header. The individual files are organised into archives covering
10° wide strips of the Glactic plane.
| Galactic Longitude | Download Catalogue |
| 30° ≤ l < 40° | A_samp_030.tar.gz (40 MB) |
| 40° ≤ l < 50° | A_samp_040.tar.gz (43 MB) |
| 50° ≤ l < 60° | A_samp_050.tar.gz (50 MB) |
| 60° ≤ l < 70° | A_samp_060.tar.gz (55 MB) |
| 70° ≤ l < 80° | A_samp_070.tar.gz (33 MB) |
| 80° ≤ l < 90° | A_samp_080.tar.gz (26 MB) |
| 90° ≤ l < 100° | A_samp_090.tar.gz (30 MB) |
| 100° ≤ l < 110° | A_samp_100.tar.gz (31 MB) |
| 110° ≤ l < 120° | A_samp_110.tar.gz (27 MB) |
| 120° ≤ l < 130° | A_samp_120.tar.gz (29 MB) |
| 130° ≤ l < 140° | A_samp_130.tar.gz (26 MB) |
| 140° ≤ l < 150° | A_samp_140.tar.gz (17 MB) |
| 150° ≤ l < 160° | A_samp_150.tar.gz (25 MB) |
| 160° ≤ l < 170° | A_samp_160.tar.gz (28 MB) |
| 170° ≤ l < 180° | A_samp_170.tar.gz (26 MB) |
| 180° ≤ l < 190° | A_samp_180.tar.gz (23 MB) |
| 190° ≤ l < 200° | A_samp_190.tar.gz (25 MB) |
| 200° ≤ l < 210° | A_samp_200.tar.gz (22 MB) |
| 210° ≤ l < 215° | A_samp_210.tar.gz (14 MB) |
A catalogue of stellar parameters
In adition to estimating the three
dimensional distribution of extinction, H-MEAD also infers the
fundamental parameters of stars in the catalogue employed.
By publishing only expectations and one
dimensional standard deviations we are passing on only a relatively
crude depiction of the posterior probability distribution. Consequently
features such as multimodality of the posterior and covariance between
parameters will not be apparent. Additionally, the calculation of the
stellar parameters has been subject to both a set of priors and a survey
selection function, both of which have heavily shaped the results
obtained. Any further analysis of these data will also be inevitably
subject to these same priors and selection function. In light of these
factors, we caution the reader that care must be taken not to
over-interpret or mistake patterns which appear in this catalogue. These
data are provided in the spirit that they may be a useful resource for
gaining insight into the origin of features in the extinction map.
Download
We provide one file that contains the entire catalogue (1.5GB).
We also split the catalogue up into files
corresponding to each sightline analysed. These files detail the
Galactic longitude and latitudes covered in the file header. The
individual files are organised into archives covering 10° wide strips of
the Glactic plane.
| Gal. Lon. | Download Catalogue |
| 30° ≤ l < 40° | star_cat_030.tar.gz (125 MB) |
| 40° ≤ l < 50° | star_cat_040.tar.gz (140 MB) |
| 50° ≤ l < 60° | star_cat_050.tar.gz (159 MB) |
| 60° ≤ l < 70° | star_cat_060.tar.gz (159 MB) |
| 70° ≤ l < 80° | star_cat_070.tar.gz (97 MB) |
| 80° ≤ l < 90° | star_cat_080.tar.gz (76 MB) |
| 90° ≤ l < 100° | star_cat_090.tar.gz (87 MB) |
| 100° ≤ l < 110° | star_cat_100.tar.gz (88 MB) |
| 110° ≤ l < 120° | star_cat_110.tar.gz (67 MB) |
| 120° ≤ l < 130° | star_cat_120.tar.gz (70 MB) |
| 130° ≤ l < 140° | star_cat_130.tar.gz (62 MB) |
| 140° ≤ l < 150° | star_cat_140.tar.gz (38 MB) |
| 150° ≤ l < 160° | star_cat_150.tar.gz (48 MB) |
| 160° ≤ l < 170° | star_cat_160.tar.gz (62 MB) |
| 170° ≤ l < 180° | star_cat_170.tar.gz (52 MB) |
| 180° ≤ l < 190° | star_cat_180.tar.gz (47 MB) |
| 190° ≤ l < 200° | star_cat_190.tar.gz (51 MB) |
| 200° ≤ l < 210° | star_cat_200.tar.gz (51 MB) |
| 210° ≤ l < 215° | star_cat_210.tar.gz (31 MB) |
Column definitions
| Column | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | Sexagesimal, equatorial position-based source name in the form: JHHMMSS.ss+DDMMSS.s. The full naming convention for IPHAS DR2 sources has the form “IPHAS2 JHHMMSS.ss+DDMMSS.s”, where “J” indicates the position is J2000. | |
| l | degrees | Galactic longitude. |
| b | degrees | Galactic latitude. |
| s | parsecs | Mean of the marginal posterior distribution of the distance to the star. |
| d_s | parsecs | Standard deviation of the marginal posterior distribution of the distance to the star. |
| A | Mean of the marginal posterior distribution of the extinction to the star. Expressed in terms of A0, the monochromatic extinction at 5495 Å. | |
| d_A | Standard deviation of the marginal posterior distribution of the extinction to the star. Expressed in terms of A0, the monochromatic extinction at 5495 Å. | |
| logT | Mean of the marginal posterior distribution of the base-10 logarithm of the star’s effective temperature, in Kelvin. | |
| d_logT | Standard deviation of the marginal posterior distribution of the base-10 logarithm of the star’s effective temperature, in Kelvin | |
| logg | Mean of the marginal posterior distribution of the star’s surface gravity. | |
| d_logg | Standard deviation of the marginal posterior distribution of the star’s surface gravity. | |
| M | M☉ | Mean of the marginal posterior distribution of the star’s initial mass. |
| d_M | M☉ | Standard deviation of the marginal posterior distribution of the star’s initial mass. |
(sources:iphas.org)
IPHAS is complemented by the UVEX survey in the north and the VPHAS+ survey in the south.
219 million stars: a detailed catalogue of the visible Milky Way,
16 September 2014, by Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Journal Ref:
The second data release of the INT Photometric Ha Survey of the Northern
Galactic Plane (IPHAS DR2). MNRAS, September 15, 2014.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar